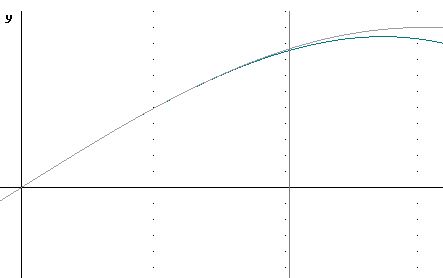
Calculus
II Class 04/02
Find the error in the third-degree Taylor
polynomial approximation to sin(pi/3).
Sin(x) = x – x^3 / 3! + x^5 /5! - x^7 / 7! +
…
So
P3(x) = x – x^3 / 3!.
P3(pi/3) = (pi/3) – (pi/3)^3 / 3! = pi/3 –
pi^3 / (3^3 * 3!) = pi/3 – pi^3 / 162 = .856.
The actual value of sin(pi/3) is sqrt(3) / 2 =
1.732 / 2 = .866.
Our error is .010.
The figure below depicts the functions y = sin(x) and y = x - x^3 / 3!. The vertical line is at x = pi/3.
What is the next derivative after the third
derivative in the Taylor expansion of sin(x)? How big can this term get between 0 and pi/3?
We got the third term x^3 / 3! by evaluating
–cos(x) at x = 0. The next derivative is sin(x). The next term would be sin(x) / 4! * x^4 evaluated at zero
for this expansion, so the 4 th term does not appear in the
expansion. However it’s sorta
there in the background, causing errors as we move away from x = 0.
The magnitude of the maximum error possible
between x = 0 and x = pi/3 is the maximum possible magnitude of this term
between 0 and x = pi/3.
What is the maximum possible value of
·
sin(x) / 4! * x^4
between x = 0 and x = pi/3?
Sin(x) and x are both increasing between x = 0
and x = pi/3, so the max value occurs at x = pi/3.
Our max value is sin(pi/3) / 4! * (pi/3)^4 =
.0433.
Use this procedure to find the error bound
of the third Taylor polynomial approximation to y = e^x when x = .3.
Find the actual error and show that it’s within those bounds.
We begin with the third-degree polynomial
approximation
P3(x) = x + x^2 / 2! + x^3 / 3!.
Our fourth-degree term is generated by the
fourth derivative of x, which is e^x. This
gives us the function e^x / 4! * x^4. This ‘background’ function drives the error of the
third-degree approximation.
Our error bound is the maximum possible
magnitude of this ‘background’ function on the interval in question.
Since we have expanded about x = 0 and we’re looking at the
approximation for x = .3, we therefore want to find the max possible value of
e^x / 4! * x^4 on the interval (0, .3).
This ‘background’ function is formed from
the product of two increasing functions e^x and x^4. This means that the function e^x * x^4 / 4! is increasing,
and its max value is taken at x = .3.
At x = .3 the value is e^.3 * .3^4 / 4! = .
000456 approx..
The actual value of e^.3 is 1.349858807
The value of P3(x) = 1 + x + x^2 / 2! + x^3 /
3! is P3(.3) = 1.34950000.
The magnitude of the error is the magnitude of
the difference between the actual and approximated values, which is .000359
approx..
This is within the max possible error .000456.
What is the term we need in order to
estimate maximum possible error of the nth degree approximation to sin(x)?
The n+1 term of the expansion is dictated by
the n+1 derivative, which is either +-sin(x) or +-cos(x).
The error term is either | sin(x) * x^(n+1) / (n+1)! | or |cos(x) *
x^(n+1) / (n+1)! | .
For x = 10, what value of n will ensure
that (n+1)! is less than either | sin(x) * x^(n+1) | or | cos(x) * x^(n+1) |?
Since | sin x | <= 1 and | cos(x) | <= 1
we have
| sin(x) * x^(n+1) | < | x^(n+1) | and
| cos(x) * x^(n+1) | < | x^(n+1) | so it
will suffice to find n such that | x^(n+1) | < (n+1)!.
Whatever x is, let n be greater than x.
Then x^(n+1) < (n+1)^(n+1).
But (n+1)^(n+1) =(n+1) * (n+1) * (n + 1) * …
* (n + 1), where we have the factor n+1 a total of n+1 times.
(n+1) ! = (n+1) * n * (n-1) * (n-2) * … * 1.
This expression consists of n+1 terms, each
less than the corresponding (n+1) term of (n+1)^(n+1).
This does not establish that (n+1)! is greater
than (n+1)^(n+1).
So let n > 2 x. We now have x < n/2 so x^(n+1) < (n/2)^(n+1).
Now we have n/2 * n/2 * n/2 * … * n/2, where the factor n/2 is
multiplied n times.
(n+1) ! = (n+1) * n * (n-1) * (n-2) * … * 1.
So x^(n+1) / (n+1)! < [n/2 * n/2 * n/2 *
… * n/2 ] / [ (n+1) ! = (n+1) * n * (n-1) * (n-2) * … * 1 ]
= (1 / 2)^(n+1) * n / (n+1) * n / (n) * n /
(n-1) * … * n / 1.
Now if we increase n by 1 we get another
factor of 1 / 2 , and we get the term (n+1) / (n+2).
Since (n+1) / (n+2) < 1, our new expression
is less than 1 / 2 of the previous expression.
We can therefore make our expression as small
as we wish by increasing n.