Experiment 19, Modified: When two objects moving along a common straight line
collide and maintain motion along the same line as before collision, the total of their
momenta immediately after collision is equal to the total immediately before collision.
By setting up head-on collisions of various spherical objects and allowing
them immediately after collision to fall a known distance under the influence of gravity,
we can from the horizontal ranges of their falls determine their velocities immediately
after collision. If one object is stationary prior to collision, and if the velocity
of the other immediately before collision is determined, we can then compare total
momentum before collision to total momentum after. This comparison constitutes a
test of the Law of Conservation of Momentum for two objects.
See CD EPS01 for Lab Kit Experiment 19. Note that the setup here has been
adapted somewhat from the version on the video clip; however the differences and
similarities should be easy to understand.
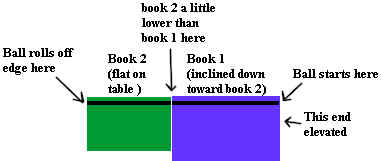
In this experiment we will allow the larger marble in the kit to roll from rest
down the binding indentation of a hardcover book inclined at an angle, then onto the
binding indentation of another book lying flat on a horizontal tabletop. This
setup replaces the curved-end incline seen in the video clips. The setup of the
books is shown in the figure below.
Note that the binding indentation in recent printings of
the book might not be deep enough to keep the marble 'in the groove'. If
this is the case for your book you can make the following adaptation:
- Crease a strip of paper, with the crease about 1/2 inch
from its edge.
- If started from the middle of the 'high end' of the book
the ball will roll toward the lower end, and probably will also tend to roll
toward the binding edge of the book. If not you can tilt the book very
slightly toward the binding edge to ensure that this happens.
- If you place the creased edge of the paper parallel to
the indentation but on the flat surface of the book, that will be sufficient
to keep the marble rolling in a straight line. The strip of paper should
lie flat on the book, with the plane of the 1/2-inch crease in the upward
direction and sloping slightly away from the path of the marble.
- Do this for both books.
- The right end of the 'blue' book is elevated so the marble will achieve a
significant velocity while rolling down the binding indentation. If the book is not
moved we can expect the marble to achieve very nearly the same velocity with every trial.
- The books will be aligned so that the marble rolls from the binding indentation
of the 'blue' book directly and without interruption onto the binding indentation of the
'green' book. The 'green' book will not quite be as thick as the 'blue' book so that
the marble will drop smoothly from the first book to the second.
- The marble will roll with significant velocity off of the second book, which will
be lying flat on a horizontal table. The velocity of the marble as it exits the
second book is expected to be very nearly the same from trial to trial.
The setup is illustrated below:
The setup with creased strips of paper:
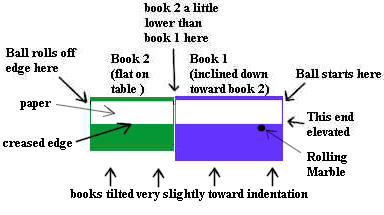
End view of book with creased paper and marble:

The marble, referred to hereafter as the 'ball', will roll down the
two books and strike another marble
(also called a ball) head-on, after which both balls will fall as projectiles to the
floor. We will obtain data to determine the velocities of the balls after impact and the
velocity of the first ball before impact, from which we can make various tests of the
conservation of momentum.
You will collide two balls of unequal mass, with the larger ball rolling down
the incline and the smaller set up as a stationary target.
- Using a section of a straw, as in the video clip, set up the smaller ball at the
edge of a table just past the end of the ramp (i.e., the two-book system described above).
Position the ball also that the collision will be head-on in both a horizontal and a
vertical plane.
- Position sheets of paper overlaid with carbon paper to detect the positions at
which the balls strike the floor. If carbon paper is not available devise another
method for determining with reasonable accuracy the positions at which the balls strike
the floor.
- Release the larger ball from the end of the ramp and allow it to collide with the
'target' ball, after which the two balls will fall to the floor and, if carbon paper is
availabe, leave marks indicating the positions at which they struck.
- Take any other data you will need to determine the velocities of the balls
immediately after collision.
- Using the same procedures as in previous experiments, determine the horizontal
velocities of the falling balls. [These procedures are based on the projectile
properties of each ball; measuring the horizontal range of the ball and the distance of
fall you analyze the vertical motion (which should have initial velocity zero if the balls
collide as instructed) to determine the time of fall and then from the range determine the
horizontal velocity.]
- Allow the ball rolling down the incline to fall freely without colliding with the
second ball, and collect the data you will need to determine the velocity with which it
left the ramp.
- Determine the horizontal velocity of the ball as it falls.
- Letting m1 stand for the mass of the larger ball and m2 for the mass of the
smaller, write expressions for the total momentum of the two balls before collision and
after collision.
- Set the two expressions equal to obtain an equation expressing momentum
conservation.
- The resulting equation will have m1 and m2 as unknowns.
- Using simple algebra, rearrange the equation to get only the ratio m2 / m1 on the
left-hand side. The other side will reduce to a single number, which will be the ratio m2
/ m1 of the mass of the smaller to the larger ball.
- What do you get for the ratio?
- Measure the diameters of the two balls. Is the ratio of the masses equal to the
cube of the ratio of the diameters? If the balls are made of the same material, why would
we expect that the ratios would behave in this manner?
Using the program MOMSIM (available on the 164.106.222.236 homepage under
Simulations), analyze the first collision from a variety of reference frames.
- Enter the velocities and the mass ratio, as requested, for the balls in the first
collision.
- If the collision is viewed from a vehicle which is moving smoothly along with the
moving ball just before collision, and which continues moving smoothly at this velocity,
then to an occupant of the vehicle it will appear that the this ball is initially standing
still and that the second ball approaches and strikes the first. After collision the first
ball will appear to move 'backwards'.
- Using the simulation, give your vehicle a velocity equal to that of the moving
ball just before collision, and observe the collision from this frame of reference.
Describe what you see and why what you see makes good sense as a collision.
- Now use the simulation to view the collision from a vehicle which is moving at
half the before-collision velocity of the first ball. Describe what you see and why this
collision makes good sense.
- Repeat using a frame of reference of the second ball after collision.
- Verify in detail that the conservation of momentum is validated in each of these
frames of reference. Explain why the velocities are as indicated on the simulation, and
calculate total momentum before and after collision for each frame of reference.
Analyze the collision from the center-of-mass frame, using various coefficients
of restitution.
- The center of mass of the system at any given instant is the position relative to
which the two balls would balance if their positions were frozen and they were placed on a
beam rotating about the center of mass.
- As the balls move toward or away from collision, their center of mass moves in
almost every reference frame. The one frame in which the center of mass does not
move is called the center-of-mass frame.
- The total momentum in the center-of-mass frame is 0.
- If the balls were to stick together after collision, they would be moving with
the velocity of the center-of-mass frame. This velocity is easily found to be vCM =
(m1 v1 + m2 v2) / (m1 + m2).
- Determine vCM from the velocities of the balls before collision, and observe the
collision from this frame.
- Now let the computer calculate and represent the actual velocities to be expected
after collision, based on the velocities before collision. First run the simulation,
then make this choice afterwards.
- You will need to select a coefficient of restitution, which is the ratio of the
magnitude of the relative velocity of the balls after collision to that before.
Begin by selecting 0 and 1, and observe how the white dot, which is at the center of each
circle before collision, tends to move differently after collision. These white dots
represent the positions of the balls according to the computer's calculations, which are
based on the initial velocities you provided..
- See if you can find a coefficient of resitution which best models your
observations by keeping the white dots as close to the positions of the balls as possible.
- How closely were you able to model your observed velocities? How nearly
'true' then were your conclusions? How does this compare with the error in your
experiment (the degree to which your results failed to verify momentum conservation)?
Analysis of errors
- Discuss possible sources of error in this experiment.
- Estimate the possible error ranges in your data, and determine whether within the
resulting ranges of observed momenta we can conclude that momentum is conserved.


