class 050907
1. How much force would all 5 of your rubber bands exert if they were connected in parallel and stretched to 9 cm, to 10 cm, and to 11 cm? Give the total force that would be exerted at each of these lengths.
2. If we needed a force of 10 Newtons, how could we use a combination of your rubber bands to get it? Give a specific numerical answer which can be tested in class.
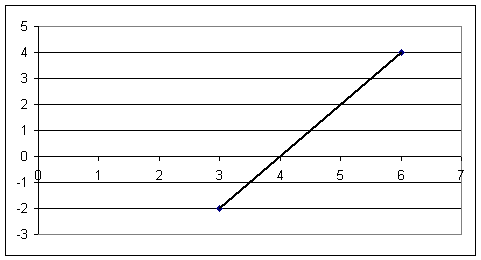
3. The graph in the figure below represents velocity in cm/s vs. clock time in sec for a marble on an incline.
Using information from the graph find the displacement during the given time interval and the acceleration of the marble.
Find the displacement of the marble between clock times t = 3 sec and t = 4 sec.
Find the displacement of the marble between clock times t = 4 sec and t = 5 sec.
Find the displacement of the marble between clock times t = 5 sec and t = 6 sec.

Use your results to plot a graph of the marble's position in cm vs. clock time in sec.
4. The figure below depicts force in Newtons vs. length in cm for a certain rubber band:
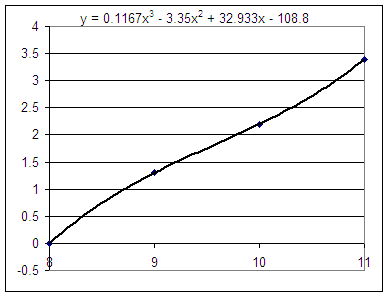
Estimate the area beneath the graph from L = 8 to L = 9.
Estimate the area beneath the graph from L = 9 to L 10.
Estimate the area beneath the graph from L = 10 to L = 11.
What is the area beneath the graph between L = 8 and L = 10?
What is the area beneath the graph between L = 8 and L = 11?
Make a table of the area beneath the curve between length 8 and length L vs. L:
| L | area between length 8 and length L |
Sketch a graph of area beneath the curve between length 8 and length L vs. L:
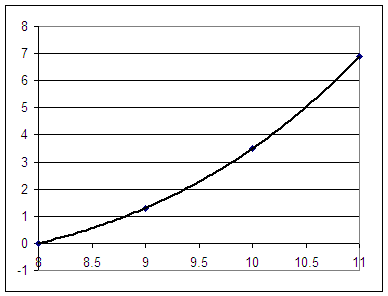
What is the average force bewteen lengths of 8 cm and 9 cm? What do you get when you multiply this average force by the 1 cm displacement between 8 cm and 9 cm?
What is the average force bewteen lengths of 8 cm and 10 cm? What do you get when you multiply this average force by the 2 cm displacement between 8 cm and 10 cm?
What is the average force bewteen lengths of 8 cm and 11 cm? What do you get when you multiply this average force by the 3 cm displacement between 8 cm and 11 cm?
5. 2, 3, 4 dominoes with hook (gorilla glue and dominoes, or hot glue); sliding range and proj range vs. ave force * dist
range vs. pullback, force vs. pullback, range vs. force, running area vs. force
range can be projectile range or sliding range
How do we come up with the average velocity? Also, do you
always have to sketch a graph to come up with the angular
acceleration or is it just helpful?
Average velocity is defined as the average rate of change of position with
respect to clock time, and average acceleration is the average rate of change of
velocity with respect to clock time.
We come to understand these concepts by thinking about them numerically,
graphically, symbolically and verbally. All four modes of understanding are
necessary. While we can work out a problem in any one of these ways, that we
reason out the problem in all four ways. This leads us to the deeper
understanding we'll need in order to solve complex problems and our
understanding.
4. The figure below depicts force in Newtons vs. length in cm for a certain rubber band:

Estimate the area beneath the graph from L = 8 to L = 9.
Estimate the area beneath the graph from L = 9 to L 10.
Estimate the area beneath the graph from L = 10 to L = 11.
What is the area beneath the graph between L = 8 and L = 10?
What is the area beneath the graph between L = 8 and L = 11?
Make a table of the area beneath the curve between length 8 and length L vs. L:
| L | area between length 8 and length L |
Sketch a graph of area beneath the curve between length 8 and length L vs. L:


What is the average force bewteen lengths of 8 cm and 9 cm? What do you get when you multiply this average force by the 1 cm displacement between 8 cm and 9 cm?
What is the average force bewteen lengths of 8 cm and 10 cm? What do you get when you multiply this average force by the 2 cm displacement between 8 cm and 10 cm?
What is the average force bewteen lengths of 8 cm and 11 cm? What do you get when you multiply this average force by the 3 cm displacement between 8 cm and 11 cm?
5. 2, 3, 4 dominoes with hook (gorilla glue and dominoes, or hot glue); sliding range and proj range vs. ave force * dist
range vs. pullback, force vs. pullback, range vs. force, running area vs. force
range can be projectile range or sliding range