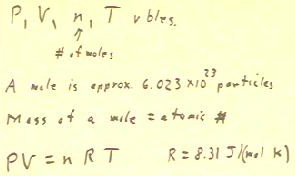"
Physics II
Class Notes, 1/15/99
The Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law tells us how the pressure P, volume
V, number of moles n and absolute temperature T
of a gas are related.
- A mole is a fixed number of particles,
approximately equal to 6.02 * 10^23 particles (check your text for a more
precise number).
- The number of particles in a mole is called Avagadro's Number.
- The mass of a mole of an element is equal to the atomic
number, in grams.
- The mass of a mole of a chemical compound is equal to the molecular
mass number, in grams.
The Ideal Gas Law summarizes our experience of gases,
where we observe the following:
- When the number of moles and the temperature of a
confined gas are held constant, then pressure increases when
volume decreases and decreases when volume increases.
We say that in this case pressure and volume are inversely
proportional, so that the product PV is constant.
- We can keep the number of moles constant by not
allowing any gas to escape or enter a container.
- We can keep the temperature constant by keeping the container at the same
temperature as its constant-temperature surroundings (e.g., a
container in a room at constant temperature); we do this by making changes slowly enough
that the temperature of the container remains in equilibrium with the room
temperature.
- When number of moles n and temperature T are held constant,
then for example when we compress the gas to decrease V,
the pressure P must increase.
PV = constant clearly implies that an increase in one
of the two quantities is associated with a proportional decrease in the
other.
- If we hold the volume of a fixed amount of gas constant, then pressure increases or
decreases with absolute temperature.
- We hold the volume constant by confining the gas to a rigid
container.
- We hold the amount of gas constant by keeping the container sealed.
- When we add thermal energy to the container and temperature
rises, we observe that the pressure increases proportional to
the absolute temperature.
We could write this proportionality P = constant * T, which implies
that the two quantities go up or down together..
- If we hold the pressure and amount of gas constant,
then the volume increases or decreases proportional to the absolute
temperature.
- We can hold the pressure of a gas constant by confining it to a cylinder
with a freely moving piston which is exposed to
a constant pressure, for example to air pressure.
- We hold the amount of gas, i.e., the number of moles,
constant by not allowing any gas to leak into or out of the
system.
- We then observe that the gas expands or contracts as temperature
is changed, with volume proportional to absolute
temperature.
We can write this proportionality as V = constant * T.
These behaviors are summarized in one law, the Ideal Gas Law,
which states that PV = nRT.
The quantity R is a universal constant equal to
approximately 8.31 Joules/(mole Kelvin).
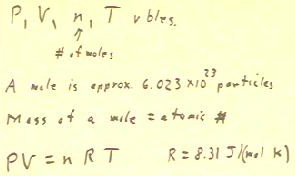
In Experiment 4, we had two connected systems, each with its own characteristics,
each thermally isolated from the other while being affected by a force
exerted by the other.
One system consisted of the constant mass of gas on the bottle side of
the alcohol column.
- We changed the temperature of this system by transferring
thermal energy into or out of the system while its volume and quantity
of gas remained nearly constant (the change in volume
corresponded to the changing volume of tubing in the system as the
alcohol column moved, and to the thermal expansion or contraction of the container
itself).
- These changes in volume were small compared to the total volume of the
container, so to a reasonabe degree of precision the volume remained constant.
- Gas did not enter or leave the container, so the number
of moles remained constant.
- We therefore expect that pressure and temperature are nearly
proportional for this system.
The other system consisted of the gas in the tube between the alcohol column and
the sealed end of the tube.
- This system, if protected from contamination by our thermal
energy sources, should remain at very nearly at the temperature
of the room. The small amount of thermal energy
transferred through the alcohol should be mostly dissipated through
the walls of the tubing.
- Since the system remains sealed by alcohol at one end and by the seal
at the other, the number of moles of gas remains constant.
- Since PV = nRT, and since n, R and T are constant, it
follows that PV = nRT = constant, so PV = constant, as indicated below.
- We often compare two states of a gas, designating then this state
1 and state 2.
- In Experiment 4, for example, state 1 might be the state of the system before
the gas in the bottle (not in the air column) is heated and
state 2 the state after heating.
- P1 and V1 would be the pressure and volume in the air
column before, and P2 and V2 the pressure in volume after
the transfer of thermal energy to the gas in the bottle.
- (P changes as a result of the changing force exerted by the gas
in the bottle on the alcohol, and through the alcohol on the air
column.)
- In this case we would say that since PV is constant,
then for the air colulmn (not the gas in the bottle) P1 * V1 = P2 * V2.
- We note that PV = const implies that P = const / V.

In the bottle, we have n and V constant, as we saw
above; we therefore expect P and T to be the changing
quantities.
- We could therefore rearrange PV = nRT so that the constant factors n
and V are on one side of the equation along with our constant R, while
our changing quantities P and T are on the other side.
- The rearranged equation would read P / T = n R / V = constant, so we
have P / T = constant.
- We would therefore conclude that for any two states of a system, P1 / T1 = P2 /
T2.
- We would also conclude that P = constant * T, that for this arrangement
pressure and temperature are proportional.
A similar strategy would be used for other cases. For example,
- Where P and n are constant we would obtain V / T = n R / P = constant, V1 / T1 =
V2 / T2, or V = constant * T.
- Where P and T are constant, we would have V / n = constant, V1 / n1 = V2 / n2, or
V = constant * n (this situation might corresond to adding gas to a system at constant
pressure and temperature, which would require increased volume).
"