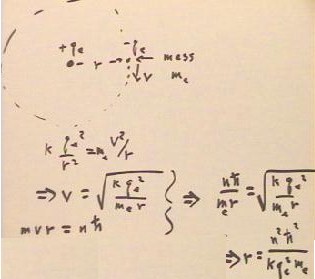
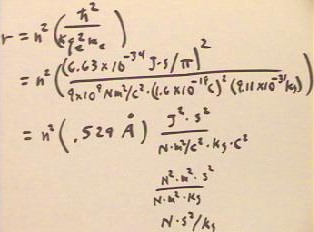
Setting the expression for the Coulomb force equal to the expression for the centripetal force and applying the condition of quantization on the angular momentum, we again obtain the expressions for allowed orbital radii rn and orbital velocities vn, where n = 1, 2, 3, .... We obtain the expressions for the potential and kinetic energies -k qe / rn and .5 m vn^2 and for the total energy of the orbiting electron. We find that the total energy is En = - 1 / n^2 * [ `me k^2 qe^4 / `hBar^2 ], which is approximately equal to - 1 / n^2 * 13.6 eV. We represent these energy levels by a schematic diagram.
We consider the charging of the ends of an initially uncharged aluminum rod when a charged PVC rod is brought near the center of the aluminum rod, and the resultant 'jumping away' of an initially uncharged conductor when it touches one of these ends. These phenomena are easily understood in terms of the free migration of charge over the surface of a conductor.
As seen in the preceding class, when an electron with charge -qe orbits a proton with charge +qe at a distance r, its velocity v is related to r by equating the Coulomb's Law force and a centripetal force on the electron.
- (Note that hBar stands for the h with the 'bar' through it, and represents h / 2 `pi).
- The factor in brackets can be evaluated by substituting the values of the constant quantities, and is found to be equal to approximately .529 * 10^-10 = .529 Angstroms.
- We thus find as before that the allowed orbital radii are r = n^2 * .529 Angstroms (approx.).
The velocity v associated with the allowed orbital radius rn = n^2 [ `hBar^2 / ( k qe^2 `me) ] is vn = k qe^2 / ( n `hBar ).
The total energy is thus equal in magnitude to the kinetic energy, but due to the greater magnitude of the (negative) potential energy the total energy is negative.
- The electron volt is the kinetic energy change of a charge qe as it is accelerated freely through a potential difference of 1 volt.
- Since qe = 1.6 * 10^-19 C, and since a volt is a Joule / Coulomb, this energy is 1.6 * 10^-19 C * 1 J / C = 1.6 * 10^-19 J.
- It is easier to imagine 13.6 eV (a bit more than the energy attained by an electron if accelerated by the potential difference of a 12-volt battery) than 2.2 * 10^-18 Joules, which we cannot relate to as directly.
The picture at the top of the figure below depicts an electron being accelerated from rest at the negative plate of a capacitor to the positive plate. The potential difference between the plates is 1 volt, so the electron to choose a kinetic energy of 1 eV. We note that the final velocity of this electron with be approximately 10^6 m/s.
We observed experimentally that when a charged PVC rod is brought near the denter of an aluminum rod, the ends of the aluminum rod have the same effect on charged objects as would the PVC rod.
It is also observed that when an uncharged conductor is brought into contact with the charged end of the aluminum rod, the conductor will tend to quickly 'jump' away from the aluminum rod.
"